Comprehensive Guide to NLP [2023 Edition]
Guide to Natural Language Processing, an Introduction to NLP [2023 Edition]
Guide to Natural Language Processing, an Introduction to NLP [2023 Edition]
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is an essential composent of Machine Learning applications today. In this guide, we'll walk you through the components of an NLP stack and its business applications.
Table of Contents
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is an interdisciplinary field focusing on the interaction between humans and computers using natural language. With the increasing amounts of text-based data being generated every day, NLP has become an essential tool in the field of data science. In this blog, we will dive into the basics of NLP, how it works, its history and research, different NLP tasks, including the rise of large language models (LLMs), and the application areas.
Natural Language Processing, what is it, again?
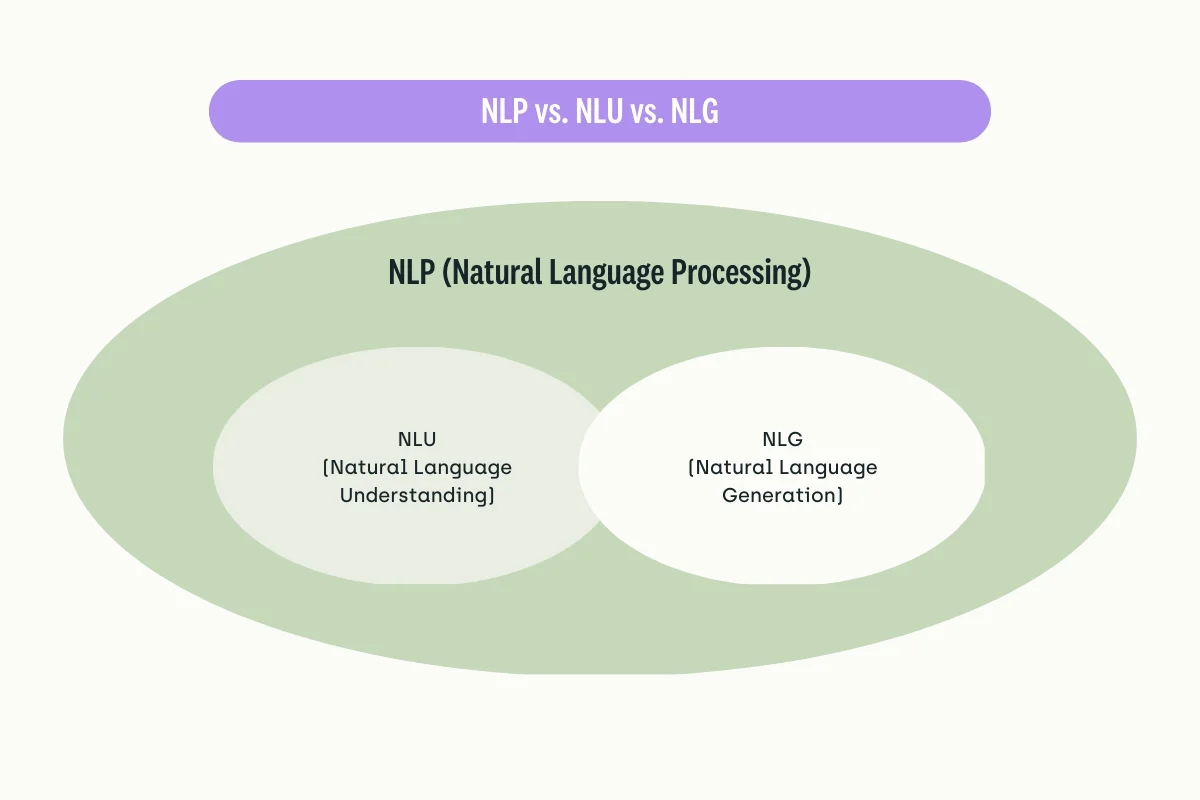
NLP is a subfield of artificial intelligence that deals with the processing and analysis of human language. It aims to enable machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language, just as humans do. This includes everything from simple text analysis and classification to advanced language modeling, natural language understanding (NLU), and generation (NLG).
NLU involves developing algorithms and models to analyze and interpret human language, including spoken language and written text. The goal of NLU is to enable machines to understand the meaning of human language by identifying the entities, concepts, relationships, and intents expressed in a piece of text or speech. Some common tasks in NLU include sentiment analysis, named entity recognition, semantic parsing, and machine translation.
NLG involves developing algorithms and models to generate human-like language, typically responding to some input or query. The goal of NLG is to enable machines to produce text that is fluent, coherent, and informative by selecting and organizing words, phrases, and sentences in a way that conveys a specific message or idea. Some common tasks in NLG include text summarization, dialogue generation, and language translation.
To summarize, NLU is about understanding human language, while NLG is about generating human-like language. Both areas are important for building intelligent conversational agents, chatbots, and other NLP applications that interact with humans naturally.
How does NLP work?
NLP techniques can be divided into two broad categories: rule-based systems and machine-learning systems. Rule-based systems rely on pre-defined rules and linguistic knowledge to process text, while machine learning systems use statistical algorithms and models to learn patterns from data and improve their accuracy over time.
NLP works by breaking down language into its smallest units (words, phrases, sentences) and analyzing the structure and meaning of those units. It can involve different steps:
Tokenization
Tokenization is the process of breaking down a piece of text into individual words or phrases, known as tokens. This is typically the first step in NLP, as it allows the computer to analyze and understand the structure of the text. For example, the sentence "The cat sat on the mat" would be tokenized into the tokens "The", "cat", "sat", "on", "the", and "mat".

Part-of-speech tagging
Part-of-speech tagging is the process of identifying the grammatical structure of each word or phrase in a piece of text. This involves labeling each token with its part of speech, such as noun, verb, adjective, etc. This information is important for understanding the meaning of the text, as different parts of speech can convey different meanings. For example, in the sentence: "The cat sat on the mat", "cat" is a noun, "sat" is a verb, and "the" is a determiner.

Syntactic analysis
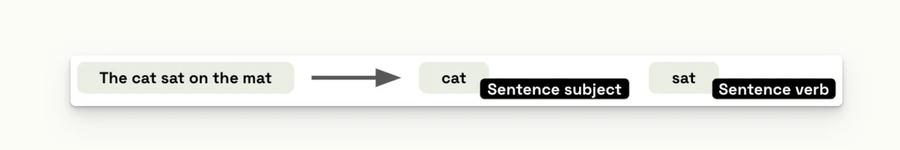
Syntactic analysis, also known as parsing, is the process of analyzing the grammatical structure of a sentence to identify its constituent parts and how they relate to each other. This involves identifying the different parts of speech in a sentence and understanding the relationships between them. For example, in the sentence "The cat sat on the mat", the syntactic analysis would involve identifying "cat" as the subject of the sentence and "sat" as the verb.
Semantic analysis
Semantic analysis is the process of understanding the meaning of a piece of text beyond just its grammatical structure. This involves analyzing the relationships between words and phrases in a sentence to infer meaning. For example, in the sentence "I need to buy a new car", the semantic analysis would involve understanding that "buy" means to purchase and that "car" refers to a mode of transportation.

These techniques are all used in different stages of NLP to help computers understand and interpret human language.
Natural Language Processing History and Research
NLP has a long history, dating back to the 1950s. The early years were focused on rule-based systems and symbolic methods, such as Chomsky’s generative grammar, that aimed to represent language using formal rules. In the 1980s and 90s, machine learning methods gained popularity, introducing statistical models such as Hidden Markov Models (HMMs) and Conditional Random Fields (CRFs). More recently, the development of deep learning and neural networks has revolutionized NLP, leading to the creation of large language models (LLMs) such as BERT, GPT, and T5, which we will explore further in section 6.
NLP tasks & models
NLP encompasses a wide range of tasks, including but not limited to:
Speech recognition: converting audio speech into text
Named Entity Recognition (NER): identifying and categorizing entities such as people, organizations, and locations in a text
Sentiment analysis: identifying the tone or sentiment behind a piece of text
Machine translation: translating text from one language to another
Text classification: categorizing text into predefined categories
Question answering: answering natural language questions posed by users
Text summarization: generating a summary of a longer piece of text
These tasks can be achieved by different models types; here are the most common ones:
Rule-based models: Rule-based models use a set of pre-defined rules to analyze and process text data. These rules can be based on grammar, syntax, or other linguistic rules. Tasks associated with rule-based models include tokenization, part-of-speech tagging, and named entity recognition.
Statistical models: Statistical models use probabilistic algorithms to analyze and process text data. These models are often based on machine learning algorithms such as decision trees, support vector machines, and hidden Markov models. Tasks associated with statistical models include sentiment analysis, topic modeling, and machine translation.
Neural network models: Neural network models use deep learning algorithms to analyze and process text data. These models are often based on recurrent neural networks (RNNs), convolutional neural networks (CNNs), and transformer models. Tasks associated with neural network models include natural language generation, question answering, and text classification.
Transformer models: Transformer models are a type of neural network model that has become increasingly popular recently. They are designed to process sequential data, such as text, by creating attention mechanisms that allow the model to focus on different parts of the sequence. Tasks associated with transformer models include language modeling, machine translation, and summarization.
Overall, each model type has its strengths and weaknesses, and the best model for a particular task will depend on factors such as the amount and type of data available, the complexity of the task, and the desired level of accuracy.
Focus on Large Language Models (LLMs) in NLP
LLMs are a type of machine learning model that uses deep neural networks to learn from vast amounts of text data. These models have transformed NLP, allowing for more accurate and efficient language processing, and have been at the forefront of recent breakthroughs in NLP research.
The principle behind LLMs is to pre-train a language model on large amounts of text data, such as Wikipedia, and then fine-tune the model on a smaller, task-specific dataset. This approach has proven to be highly effective, achieving state-of-the-art performance on many NLP tasks.
Training an LLM requires a large amount of labeled data, which can be a time-consuming and expensive process. One way to mitigate this is by using the LLM as a labeling copilot to generate data to train smaller models. This approach has been used successfully in various applications, such as text classification and named entity recognition.
Natural Language Processing applications - why is it important?
NLP has numerous applications in various industries, including healthcare, finance, marketing, and customer service. Here are some of the key NLP use cases:
Chatbots
Chatbots are virtual assistants that use NLP to understand natural language and respond to user queries in a human-like manner. They can be used for customer service, sales, and support and have become increasingly popular recently. For example, a chatbot can help a customer book a flight, find a product, or get technical support.
Spam detection
NLP can be used to identify and filter spam emails or messages. By analyzing the text of an email or message, NLP algorithms can identify spam keywords or patterns and flag them for further action.
Text summarization
NLP can be used to automatically summarize long documents or articles into shorter, more concise versions. This can be useful for news aggregation, research papers, or legal documents.
Sentiment analysis
NLP can be used to analyze the sentiment or emotion behind a piece of text, such as a customer review or social media post. This information can be used to gauge public opinion or to improve customer service.
Named Entity Recognition (NER)
NER is used to identify and extract named entities such as people, organizations, and locations from text data. This can be used for various applications such as social media monitoring, news analysis, and fraud detection.
Machine translation
NLP can be used to translate text from one language to another. This has numerous applications in international business, diplomacy, and education.
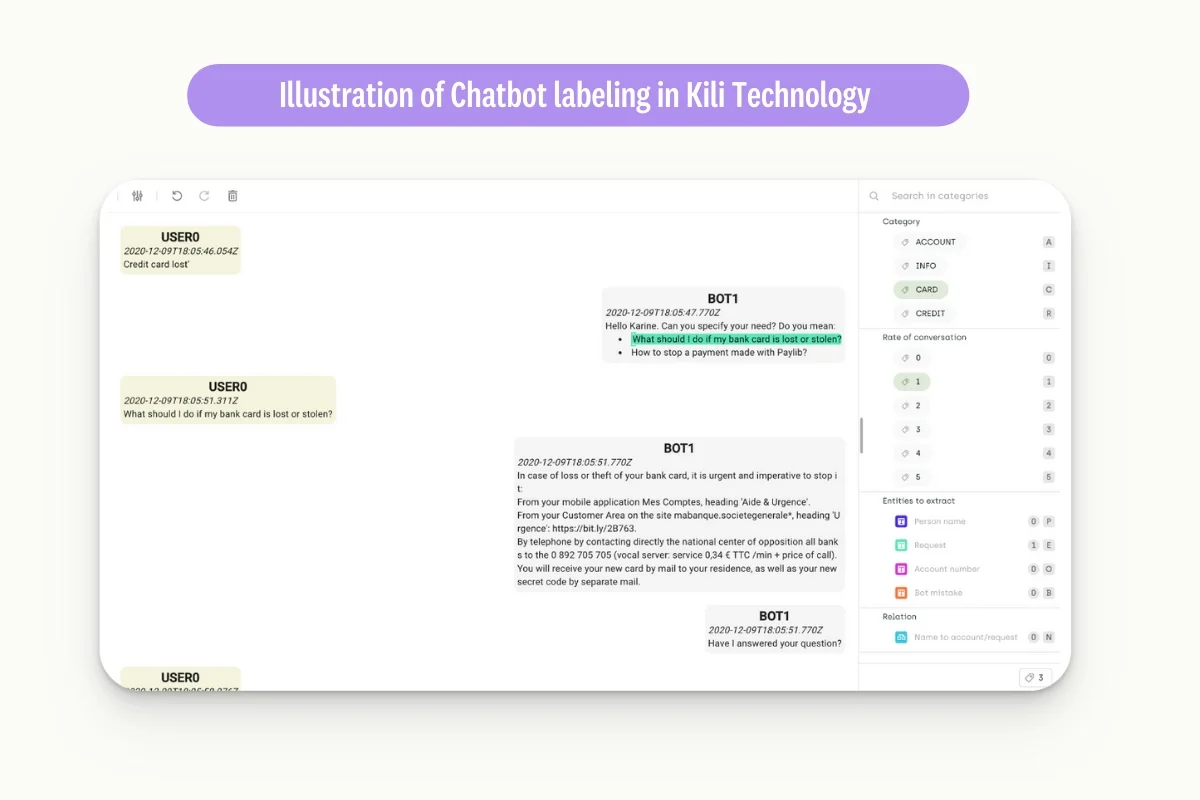
These NLP applications can be illustrated with examples using Kili Technology, a data annotation platform that allows users to label data for machine learning models. For example, to train a chatbot, users can annotate customer messages and responses using Kili, providing the data necessary to train the model to understand natural language and respond to customer queries.
Valuable NLP material: our recommendations
Natural Language Processing Datasets
On Kili Technology's GitHub, you can find a list of awesome datasets on NLP. They are split across tasks, languages,s and sectors, like the CCCS-CIC-AndMal-2020, which proposes a new comprehensive and huge android malware dataset, named CCCS-CIC-AndMal-2020 including 200K benign and 200K malware samples for a total of 400K android apps with 14 prominent malware categories and 191 eminent malware families.
In the Finance sector, SEC-filings is generated using CoNll2003 data and financial documents obtained from U.S. Security and Exchange Commission (SEC) filings.
In French on the medical sector, QUAERO French Medical Corpus was initially developed as a resource for named entity recognition and normalization.
Natural Language Processing: State-of-the-art Papers
To further improve NLP skills, various ressources are relevant:
NLP-Overview provides a current overview of deep learning techniques applied to NLP, including theory, implementations, applications, and state-of-the-art results. It's an excellent resource for researchers new to Deep NLP.
NLP-Progress tracks the advancements in Natural Language Processing, including datasets and the current state-of-the-art for the most common NLP tasks. The article "NLP's ImageNet moment has arrived" discusses the recent emergence of large pre-trained language models as a significant advancement in the field of NLP.
ACL 2018 Highlights: Understanding Representation and Evaluation in More Challenging Settings offers insights on the latest advancements in NLP, with a focus on representation and evaluation in challenging settings.
Four deep learning trends from ACL 2017. Part One: Linguistic Structure and Word Embeddings
and Four deep learning trends from ACL 2017. Part Two: Interpretability and Attention discuss trends in deep learning as applied to NLP, such as linguistic structure, word embeddings, interpretability, and attention.
Highlights of EMNLP 2017: Exciting Datasets, Return of the Clusters, and More! covers the exciting datasets and advancements in the field of NLP that were presented at EMNLP 2017.
Deep Learning for Natural Language Processing (NLP): Advancements & Trends provides insights into advancements and trends in NLP, with a focus on deep learning.
Survey of the State of the Art in Natural Language Generation is an overview of the current state of the art in Natural Language Generation, discussing the latest advancements and techniques.
Best NLP Python Libraries
There are numerous python librairies very relevant depending on the NLP task you want to achieve. Among the best ones, we can find general-purpose NLP libraries like spaCy and gensim to more specialized ones like TextAttack, which focuses on adversarial attacks and data augmentation.
There are also several libraries that are specifically designed for deep learning-based NLP tasks, such as AllenNLP and PyTorch-NLP. Continuing, some other can provide tools for specific NLP tasks like intent parsing (Snips NLU), topic modeling (BigARTM), and part-of-speech tagging and dependency parsing (jPTDP).
Additionally, there are some libraries that aim to simplify the process of building NLP models, such as Flair and Kashgari.
Also, some of the libraries provide evaluation tools for NLP models, such as Jury.
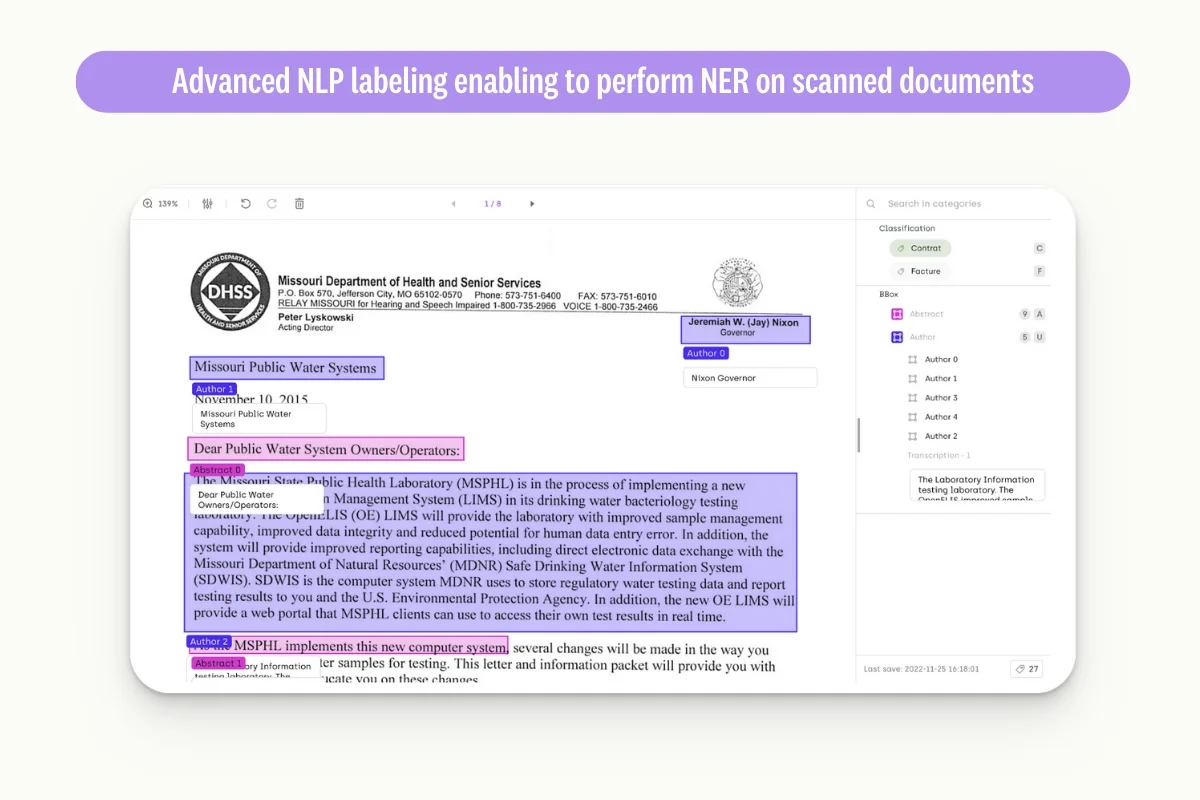
Natural Language Processing Labeling Tools
Kili Technology provides a great platform for NLP-related topics (see article on text annotation). It allows users to easily upload data, define labeling tasks, and invite collaborators to annotate the data. Kili Technology also provides a wide range of annotation interfaces and tools, including text annotation for named entity recognition, sentiment analysis, and text classification, among others. Additionally, the platform includes features for quality control and data validation, ensuring that the labeled data meets the user's requirements. With Kili Technology, NLP practitioners can save time and resources by streamlining the data annotation process, allowing them to focus on building and training machine learning models.
Best NLP MOOCs
A sample of available NLP courses can be found below:
Deep Natural Language Processing from Oxford covers topics such as language modeling, neural machine translation, and dialogue systems. The course also delves into advanced topics like reinforcement learning for NLP.
Stanford’s Deep Learning for Natural Language Processing (cs224-n) by Richard Socher and Christopher Manning covers a broad range of NLP topics, including word embeddings, sentiment analysis, and machine translation. The course also covers deep learning architectures such as recurrent neural networks and attention-based models.
Neural Networks for NLP from Carnegie Mellon focuses on neural network architectures for NLP tasks such as sentiment analysis, named entity recognition, and question answering.
Deep NLP Course by Yandex Data School covers a range of NLP topics, including sequence modeling, language models, machine translation, and text embeddings. The course also covers practical applications of deep learning for NLP, such as sentiment analysis and document classification.
fast.ai Code-First Intro to Natural Language Processing covers a mix of traditional NLP techniques such as regex and naive Bayes, as well as recent neural networks approaches such as RNNs, seq2seq, and Transformers. The course also addresses ethical issues such as bias and disinformation.
Machine Learning University - Accelerated Natural Language Processing provides a wide range of NLP topics, from text processing and feature engineering to RNNs and Transformers. The course also covers practical applications of NLP, such as sentiment analysis and text classification.
Applied Natural Language Processing lecture series is from IIT Madras. It covers NLP basics such as language modeling and text classification, as well as advanced topics such as autoencoders and attention mechanisms. The course also covers practical applications of NLP such as information retrieval and sentiment analysis.
Natural Language Processing: final thoughts
In conclusion, NLP has come a long way since its inception and has become an essential tool for processing and analyzing natural language data. With the rise of large language models, NLP has reached new heights in accuracy and efficiency, leading to numerous applications in various industries. As the amount of text data being generated increases, NLP will only become more important in enabling humans and machines to communicate more effectively.
Resources to go further on NLP
Last updated